Blogs
What is IoT Device Management? AI, Innovation & Benefits
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has revolutionized the way businesses operate. These devices, ranging from sensors and actuators to smart appliances and industrial machinery, generate vast amounts of data that drive insights and inform decision-making. However, managing this diverse array of devices efficiently and securely poses significant challenges.
Definition
IoT device management refers to the tools and processes used to provision, configure, monitor, and maintain a network of connected devices. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of your IoT assets, from initial deployment to secure decommissioning.
Importance in the IoT Ecosystem:
An effective IoT device management platform is the central nervous system of your connected ecosystem. It empowers you to:
Maximize ROI: Optimize device performance, ensure smooth operation, and gain valuable insights from collected data to drive strategic decision-making.
Enhance Security: Protect your network from cyber threats by implementing robust access controls, vulnerability management, and secure communication protocols.
Simplify Operations: Automate routine tasks like device provisioning and firmware updates, freeing up your IT team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Scale with Confidence: A robust platform can seamlessly scale to accommodate your growing network of devices, ensuring efficient management as your IoT deployments expand.
Evolution and Current Landscape:
The landscape of IoT device management has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from rudimentary tools to comprehensive platforms that empower businesses to unlock the full potential of their connected ecosystems. Here's a closer look at this journey:
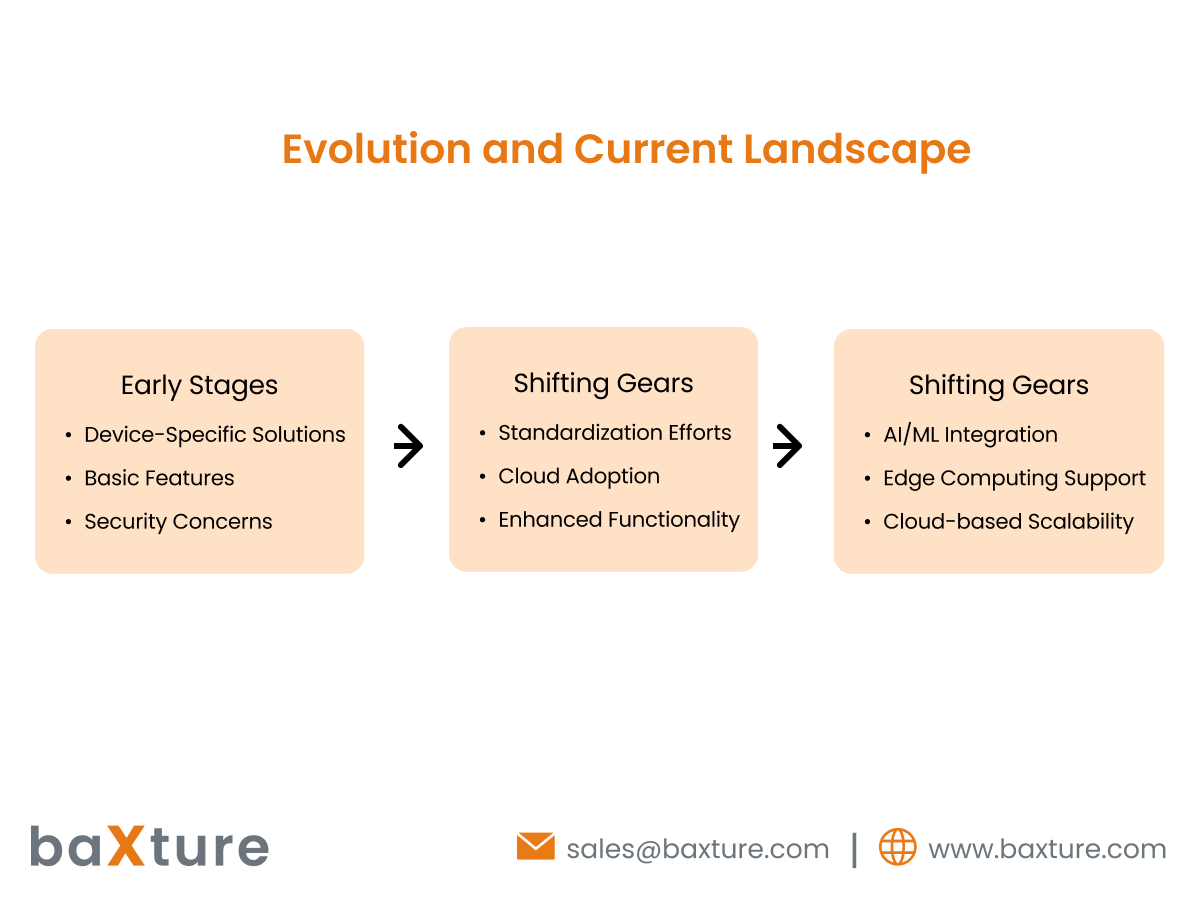
Early Stages (Limited Functionality):
- Device-Specific Solutions: Early solutions were often tied to specific device manufacturers or protocols, limiting interoperability and creating siloed management experiences.
- Basic Features: These early platforms primarily offered device provisioning, basic monitoring, and limited configuration capabilities.
- Security Concerns: Security was often an afterthought, leaving connected devices vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Shifting Gears (Emergence of Feature-Rich Platforms):
- Standardization Efforts: Industry-wide protocols and standards emerged, facilitating interoperability and enabling communication between devices from different vendors.
- Cloud Adoption: The rise of cloud computing provided a scalable and cost-effective foundation for managing large-scale IoT deployments.
- Enhanced Functionality: Platforms began offering features like remote firmware updates, over-the-air provisioning, and advanced analytics capabilities.
Current Landscape (A Symphony of Features):
- Cloud-based Scalability: Modern platforms leverage the power of the cloud to seamlessly manage vast networks of devices, ensuring efficient scalability for growing deployments.
- Advanced Analytics: Platforms now integrate with sophisticated analytics tools, enabling businesses to extract deeper insights from device data, optimize performance, and predict maintenance needs.
- Interoperability: Today's platforms boast seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure and applications, creating a unified system for managing the entire digital ecosystem.
- Security Focus: Security has become a top priority, with platforms offering robust features like access control, vulnerability management, and secure communication protocols.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cutting-edge platforms incorporate AI and ML capabilities to automate tasks, predict potential issues, and gain deeper insights from device data.
- Edge Computing Support: As edge computing gains traction, platforms are adapting to integrate with edge devices for real-time data processing and decision-making at the network's periphery.
A Glimpse into the Future
The evolution of IoT device management is far from over. Future advancements are likely to include:
- Blockchain Integration: The emergence of blockchain technology holds promise for secure data management and tamper-proof audit trails within the IoT landscape.
- Increased Automation: Platforms will become even more automated, with AI and ML playing a larger role in streamlining device management tasks.
- Focus on User Experience: Device management platforms will prioritize user experience, offering intuitive interfaces and simplifying complex configurations for non-technical users.
What is IoT Device Management?
IoT device management encompasses a set of processes, tools, and technologies designed to oversee the lifecycle of IoT devices, ensuring their optimal functionality, security, and performance. From initial provisioning and configuration to ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and updates, IoT device management covers the entire spectrum of tasks required to manage IoT deployments effectively.
How IoT Device Management Works:
At its core, IoT device management operates on the principle of centralized control and orchestration. A central management platform acts as the nerve center, providing administrators with the tools and interfaces needed to interact with and manage IoT devices across the network. Through this platform, administrators can perform various tasks such as device provisioning, configuration, monitoring, troubleshooting, and firmware updates remotely and at scale.
Fundamentals and Key Concepts:
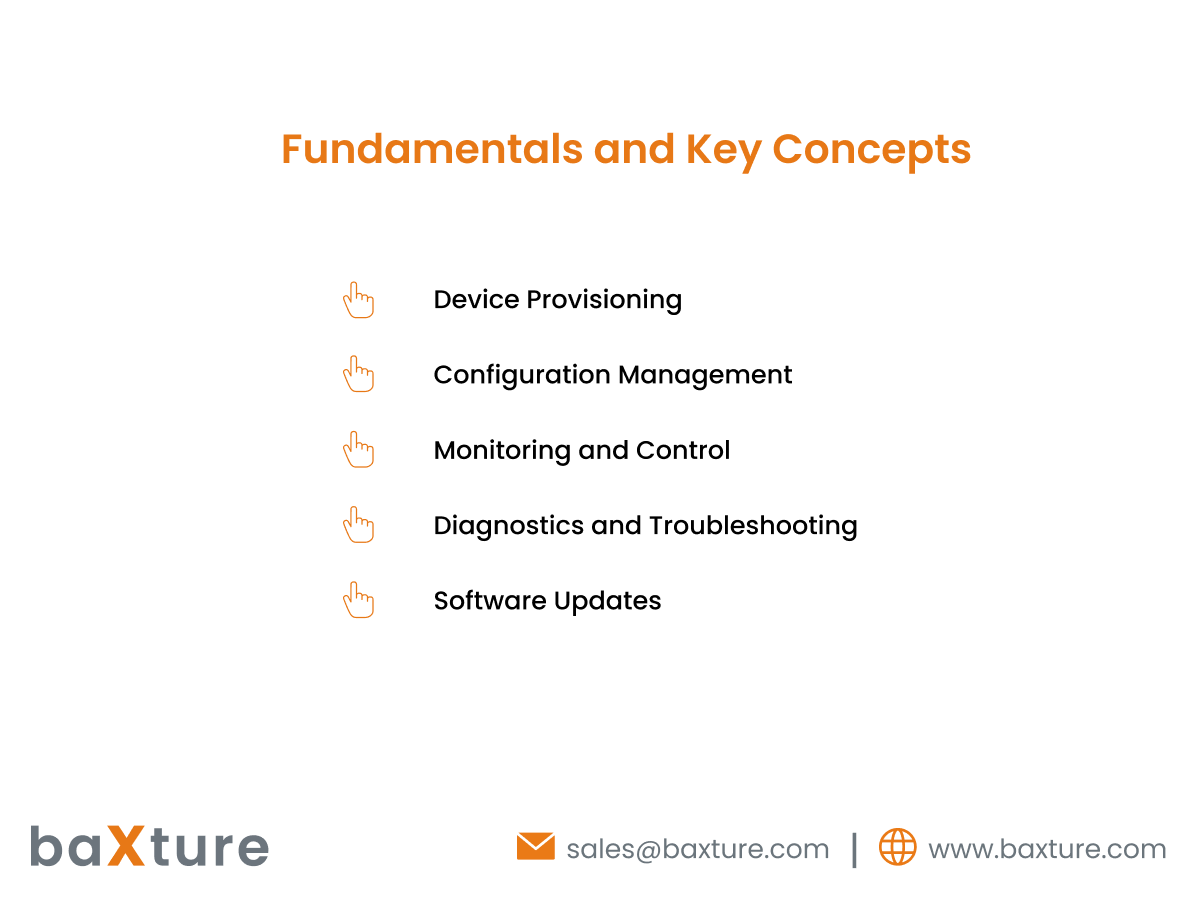
Several fundamental concepts underpin the functioning of IoT device management:
Device Provisioning: The process of onboarding new devices into the network, assigning unique identifiers, and configuring initial settings.
Configuration Management: Managing device settings and parameters to ensure they align with operational requirements and security policies.
Monitoring and Control: Continuously monitoring device health, performance, and status metrics in real-time, and exercising control over device behavior as needed.
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving issues through remote diagnostics, troubleshooting tools, and predictive analytics to minimize downtime.
Software Updates: Managing the deployment of firmware updates, patches, and software upgrades to address security vulnerabilities, introduce new features, and enhance device performance.
Tech Stack Essentials for Management:
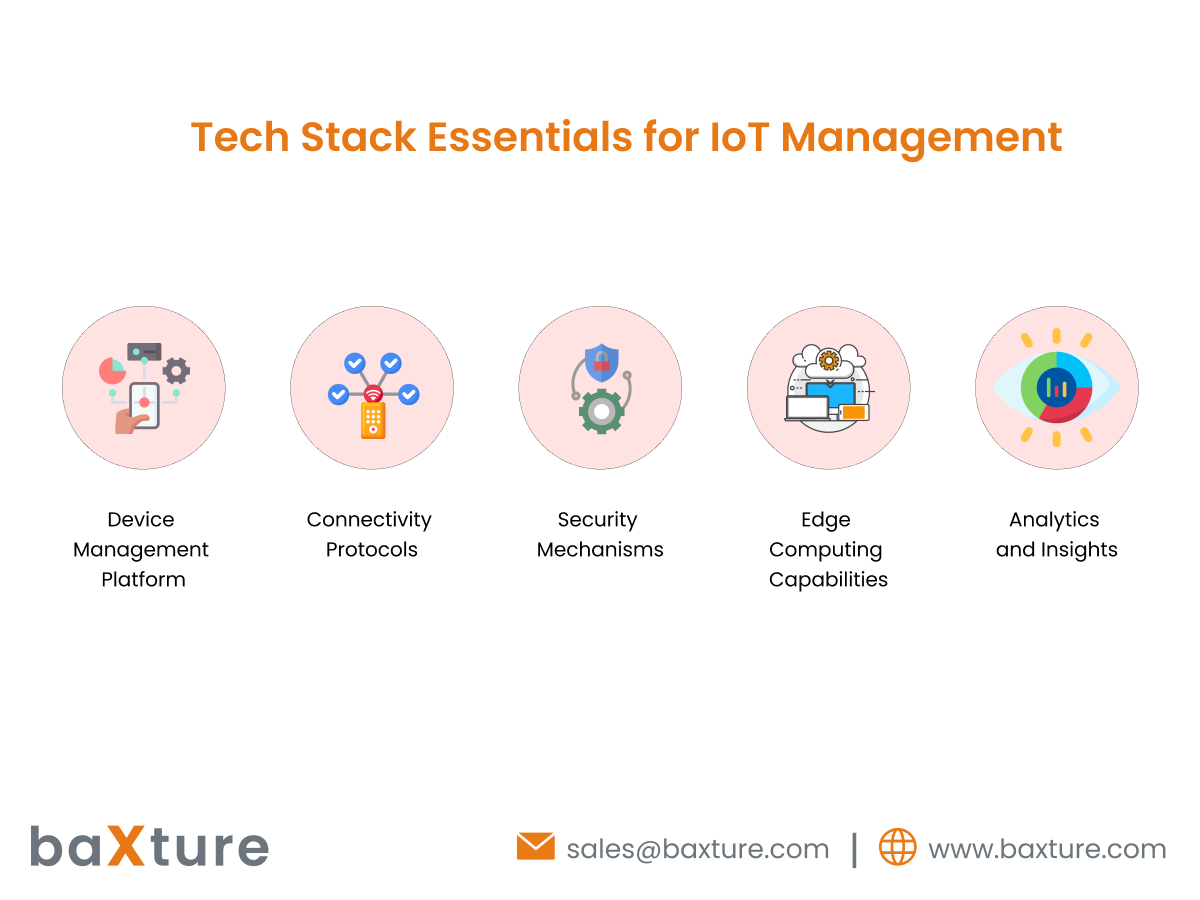
A robust IoT device management solution relies on a comprehensive tech stack that includes:
Device Management Platform: Centralized software platform for managing IoT devices, offering features such as device provisioning, configuration management, monitoring, and updates.
Connectivity Protocols: Standards and protocols for communication between devices and the management platform, such as MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP.
Security Mechanisms: Encryption, authentication, access control, and other security measures to safeguard device data and prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
Edge Computing Capabilities: Edge computing infrastructure for processing data closer to the source, enabling real-time insights and actions without relying solely on cloud resources.
Analytics and Insights: Data analytics tools and algorithms for extracting actionable insights from device data, enabling predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and optimization.
Key Features for Effective IoT Device Management
In this section, we'll explore the key features that are essential for effective IoT device management, empowering you to make informed decisions and optimize your IoT strategy.
1. Provisioning:
Efficient provisioning is the cornerstone of IoT device management. It involves the seamless onboarding of new devices into the network, assigning unique identifiers, and configuring initial settings. A robust provisioning mechanism streamlines the deployment process, reduces manual errors, and accelerates time-to-market for IoT solutions.
2. Authentication:
Ensuring the authenticity and integrity of IoT devices is paramount for maintaining a secure IoT ecosystem. Authentication mechanisms, such as digital certificates, biometric verification, and multi-factor authentication, help verify the identity of devices and establish secure communication channels, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and cyber threats.
3. Configuration Management:
Centralized configuration management enables administrators to manage device settings and parameters efficiently. From network configurations to application settings, administrators can remotely configure devices to ensure they align with operational requirements, security policies, and compliance standards. This capability enhances flexibility, scalability, and agility in IoT deployments.
4. Control and Monitoring:
Real-time control and monitoring capabilities provide visibility into the performance, health, and status of IoT devices across the network. Administrators can remotely monitor key metrics, such as temperature, humidity, and power consumption, and exercise control over device behavior as needed. This proactive approach enables early detection of anomalies, preemptive maintenance, and optimized resource utilization.
5. Diagnostics and Troubleshooting:
Effective diagnostics and troubleshooting tools are essential for maintaining the reliability and uptime of IoT deployments. Remote diagnostics enable administrators to identify and diagnose issues in real-time, minimizing downtime and service disruptions. Troubleshooting capabilities, such as remote logging, remote debugging, and automated alerts, empower administrators to resolve issues promptly and efficiently.
6. Software Updates:
Regular software updates are crucial for addressing security vulnerabilities, introducing new features, and enhancing the performance of IoT devices. A robust software update mechanism enables administrators to deploy firmware updates, patches, and software upgrades remotely and at scale. Over-the-air (OTA) updates minimize downtime, reduce operational costs, and ensure devices remain up-to-date with the latest enhancements and security patches.
7. Maintenance Procedures:
Comprehensive maintenance procedures are essential for ensuring the long-term reliability and sustainability of IoT deployments. From routine inspections to proactive maintenance tasks, administrators can implement predefined maintenance schedules and workflows to address preventive and corrective maintenance needs. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of downtime, extends the lifespan of IoT devices, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Business Benefits of IoT Device Management
In this section, we'll explore how effective IoT device management translates into enhanced operational efficiency, improved security measures, cost reduction, scalability, and regulatory compliance.
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
IoT device management streamlines operations and automates routine tasks, leading to increased efficiency and productivity across the organization. By centralizing management tasks such as provisioning, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance, administrators can optimize workflows, minimize manual intervention, and allocate resources more effectively. This results in streamlined processes, faster response times, and enhanced operational agility.
2. Improved Security Measures:
Security is a top priority in the IoT landscape, where interconnected devices are vulnerable to cyber threats and breaches. IoT device management plays a crucial role in mitigating security risks by implementing robust authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols, access control policies, and firmware updates. By proactively monitoring device health, detecting anomalies, and enforcing security policies, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, protect against cyber attacks, and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders.
3. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization:
Effective IoT device management enables organizations to optimize resource utilization, reduce operational costs, and drive bottom-line savings. By automating manual tasks, minimizing downtime, and optimizing energy consumption, organizations can achieve significant cost efficiencies. Moreover, predictive maintenance capabilities allow organizations to identify and address issues before they escalate, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of IoT assets.
4. Facilitating Scalability and Growth:
Scalability is essential for organizations looking to expand their IoT deployments and accommodate growing business needs. IoT device management provides the flexibility and scalability required to scale operations seamlessly, whether deploying new devices, expanding into new markets, or integrating with existing systems. By adopting scalable management solutions and best practices, organizations can future-proof their IoT infrastructure and support business growth initiatives with confidence.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Adherence:
In today's regulatory landscape, compliance with industry standards and regulations is non-negotiable. IoT device management helps organizations navigate complex regulatory requirements, ensuring adherence to data privacy, security, and industry-specific regulations. By implementing compliance frameworks, audit trails, and automated reporting mechanisms, organizations can demonstrate regulatory compliance, mitigate legal risks, and build trust with customers and regulatory authorities.
IoT Device Management Solutions
In this section, we'll embark on a journey to explore some of the top IoT device management software solutions available in the market today, along with additional considerations to help you make an informed decision.
Top IoT Device Management Platforms -

AWS IoT Device Management:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a comprehensive IoT device management platform that provides scalable and secure solutions for managing IoT devices at scale. With features such as device provisioning, configuration management, and over-the-air updates, AWS IoT Device Management simplifies the complexities of IoT deployments.
Azure IoT Hub:
Microsoft Azure IoT Hub is a fully managed service that enables secure and reliable communication between IoT devices and cloud applications. With support for various protocols and seamless integration with Azure services, Azure IoT Hub offers robust device management capabilities, including device provisioning, monitoring, and diagnostics.
Google Cloud IoT Core:
Google Cloud IoT Core provides a scalable and secure infrastructure for connecting, managing, and ingesting data from IoT devices. With features such as device registry, telemetry ingestion, and device state management, Google Cloud IoT Core simplifies the deployment and management of IoT solutions on Google Cloud Platform.
Hologram:
Hologram offers a flexible and scalable IoT connectivity platform that simplifies device management and communication. With features such as remote device management, real-time monitoring, and data analytics, Hologram empowers organizations to build and deploy IoT solutions with ease.
IBM Watson IoT Platform:
IBM Watson IoT Platform provides a comprehensive set of tools and services for connecting, managing, and analyzing IoT devices and data. With capabilities such as device lifecycle management, predictive maintenance, and edge analytics, IBM Watson IoT Platform enables organizations to derive actionable insights and drive business value from their IoT investments.
Oracle Internet of Things Asset Monitoring Cloud Service:
Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service offers a fully managed platform for monitoring and managing IoT devices and assets. With features such as asset tracking, condition monitoring, and predictive analytics, Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service helps organizations optimize asset performance and improve operational efficiency.
Digi Remote Manager:
Digi Remote Manager is a cloud-based IoT device management platform that provides centralized control and visibility into connected devices. With features such as remote configuration, firmware updates, and performance monitoring, Digi Remote Manager simplifies the management of distributed IoT deployments.
ServiceNow Field Service Management:
ServiceNow Field Service Management offers a comprehensive solution for managing field service operations, including IoT device management. With features such as asset tracking, predictive maintenance, and field technician dispatching, ServiceNow Field Service Management helps organizations streamline service delivery and improve customer satisfaction.
Additional Considerations When Choosing a Solution:
- Scalability: Ensure the solution can scale to accommodate your current and future IoT deployment needs.
- Security: Prioritize solutions with robust security features to protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
- Integration: Look for solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing systems and platforms to avoid compatibility issues.
- Customization: Consider solutions that offer flexibility and customization options to meet your specific requirements and use cases.
- Support and Maintenance: Evaluate the vendor's support and maintenance offerings to ensure timely assistance and updates.
- Cost: Assess the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses, to determine the solution's affordability and ROI.
Best Practices to Optimize Your IoT Deployment

Implementing IoT device management practices that ensure efficiency, security, and scalability is paramount for driving successful IoT initiatives. In this section, we'll explore implementation strategies and best practices that streamline device onboarding, configuration processes, maintenance, diagnostics, access control, data management, and analysis techniques.
1. Simplified Device Onboarding:
Simplifying the device onboarding process is essential for accelerating time-to-value and minimizing deployment complexity. Implement automated provisioning workflows and self-registration portals to streamline the onboarding of new devices into the IoT ecosystem. By automating device registration, configuration, and authentication, organizations can reduce manual errors and ensure a seamless onboarding experience for both administrators and end-users.
2. Efficient Configuration Processes:
Efficient configuration processes are critical for ensuring that IoT devices operate optimally and align with organizational requirements. Implement standardized configuration templates and profiles to streamline device configuration and ensure consistency across the IoT ecosystem. Utilize configuration management tools and policies to enforce security settings, network parameters, and operational policies, minimizing the risk of misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
3. Streamlined Maintenance and Diagnostics:
Streamlining maintenance and diagnostics workflows is essential for maximizing device uptime and minimizing operational disruptions. Implement remote monitoring and diagnostic tools that provide real-time visibility into device health, performance metrics, and operational status. Proactively monitor device telemetry data, set up automated alerts for anomalous behavior, and leverage predictive analytics to anticipate maintenance needs and prevent potential issues before they occur.
4. Ensuring Secure Access Control:
Secure access control is paramount for protecting sensitive data and mitigating security risks in IoT deployments. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) mechanisms to enforce granular access permissions based on user roles and responsibilities. Utilize strong authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric authentication to verify the identity of users and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
5. Strategies for Handling Device Proliferation:
As the number of IoT devices continues to proliferate, organizations must develop strategies to manage device scalability and complexity effectively. Implement device grouping and hierarchical organization structures to categorize and manage devices based on attributes such as location, function, or ownership. Utilize device management platforms with scalable architectures and robust APIs that can handle large volumes of devices and accommodate future growth without compromising performance or security.
6. Data Management and Analysis Techniques:
Effective data management and analysis techniques are essential for deriving actionable insights and unlocking the full potential of IoT data. Implement data governance frameworks and data lifecycle management strategies to ensure data integrity, privacy, and compliance throughout the data lifecycle. Utilize advanced analytics techniques such as machine learning, predictive analytics, and anomaly detection to extract meaningful insights from IoT data and drive informed decision-making.
Applications of IoT Device Management
In this section, we'll explore how IoT device management is transforming industries such as industrial IoT, smart city infrastructure, healthcare, consumer electronics, connected vehicles, and smart home automation.
Industrial IoT Applications:
In the industrial sector, IoT device management plays a pivotal role in optimizing operations, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring safety. From predictive maintenance and asset tracking to remote monitoring and process optimization, IoT device management enables manufacturers to gain real-time insights into equipment performance, minimize downtime, and maximize productivity. By leveraging IoT-enabled sensors, actuators, and control systems, organizations can automate workflows, streamline supply chain management, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Smart City Infrastructure IoT Application:
In smart city initiatives, IoT device management facilitates the integration and management of diverse IoT devices and sensors deployed across urban environments. From smart streetlights and traffic management systems to environmental monitoring and waste management solutions, IoT device management enables city authorities to collect, analyze, and act on real-time data to improve public services, enhance sustainability, and ensure the well-being of citizens. By deploying IoT-enabled infrastructure and leveraging data-driven insights, cities can optimize resource allocation, reduce energy consumption, and create more livable and resilient urban environments.
Healthcare:
In the healthcare sector, IoT device management is revolutionizing patient care, clinical operations, and medical device management. From remote patient monitoring and telehealth services to asset tracking and inventory management, IoT device management enables healthcare providers to deliver personalized care, improve patient outcomes, and optimize resource utilization. By connecting medical devices, wearables, and healthcare IT systems, organizations can streamline care delivery, enhance operational efficiency, and drive innovation in the healthcare industry.
Consumer Electronics:
In the realm of consumer electronics, IoT device management is driving innovation and enhancing user experiences across a wide range of devices and applications. From smart home appliances and wearable devices to connected entertainment systems and home automation solutions, IoT device management enables seamless connectivity, interoperability, and control. By integrating IoT devices with cloud-based platforms and mobile applications, organizations can offer personalized services, automate tasks, and empower consumers to interact with their devices in new and intuitive ways.
Security Considerations in IoT Device Management
In this section, we'll explore key security considerations and strategies to address security concerns, ensure data protection, manage vulnerabilities, and safeguard against cyber threats.
1. Addressing Security Concerns:
Security concerns in IoT device management encompass a wide range of risks, including unauthorized access, data breaches, device tampering, and malware attacks. Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to identify, assess, and mitigate security risks throughout the IoT lifecycle, from device provisioning and configuration to ongoing management and decommissioning.
2. Importance of Encryption and Data Protection:
Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding IoT data and communications against interception and unauthorized access. Implement strong encryption protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), to secure data in transit and at rest. Utilize robust access controls, authentication mechanisms, and data encryption techniques to protect sensitive information and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity.
3. Vulnerability Management Strategies:
Effective vulnerability management is essential for identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities in IoT devices and systems. Implement regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify weaknesses and security flaws in IoT deployments. Establish a vulnerability management process that includes vulnerability scanning, patch management, and risk prioritization to remediate vulnerabilities promptly and minimize the risk of exploitation.
4. Safeguarding Against Cyber Threats:
As IoT ecosystems become increasingly interconnected and complex, organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against evolving cyber threats. Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), firewalls, and network segmentation to detect and mitigate malicious activities. Employ threat intelligence feeds, anomaly detection algorithms, and behavioral analytics to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time. Implement security-by-design principles and adhere to industry best practices to build security into IoT devices and systems from the ground up.
Future Trends and Innovations
As C-suite executives, directors, and key decision-makers, staying ahead of emerging trends and innovations is crucial for driving strategic initiatives and maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving landscape of IoT device management. In this section, we'll explore some of the future trends and innovations shaping the future of IoT device management, including the role of AI and machine learning, edge computing integration, blockchain for enhanced security, and interoperability and standardization efforts.
Role of AI and Machine Learning:
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize IoT device management by enabling predictive analytics, proactive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of IoT data in real-time, identify patterns, and predict potential issues before they occur. Machine learning models can optimize device configurations, predict device failures, and recommend optimal actions to optimize performance and efficiency. By leveraging AI and machine learning, organizations can unlock actionable insights, drive operational efficiencies, and enhance the intelligence of IoT ecosystems.
Edge Computing Integration:
Edge computing is reshaping the IoT landscape by bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, enabling real-time processing and low-latency responses. By integrating edge computing capabilities into IoT device management solutions, organizations can reduce latency, minimize bandwidth usage, and enhance data privacy and security. Edge computing enables local data processing, analysis, and decision-making at the edge of the network, empowering organizations to derive actionable insights and respond to critical events in near real-time. By leveraging edge computing, organizations can overcome the limitations of centralized cloud computing and unlock new opportunities for innovation and efficiency in IoT deployments.
Blockchain for Enhanced Security:
Blockchain technology holds immense potential for enhancing security, trust, and transparency in IoT device management. By leveraging blockchain-based distributed ledger technology (DLT), organizations can establish immutable records of device identities, transactions, and interactions, ensuring data integrity and authenticity. Blockchain enables secure and tamper-resistant data sharing and transactions between IoT devices, stakeholders, and ecosystem participants, reducing the risk of data manipulation, fraud, and unauthorized access. By implementing blockchain-based solutions, organizations can enhance the security, resilience, and trustworthiness of their IoT deployments, paving the way for new business models and use cases.
Interoperability and Standardization Efforts:
Interoperability and standardization are critical challenges in the IoT ecosystem, where a diverse array of devices, protocols, and platforms coexist. Efforts to establish common standards, protocols, and interoperability frameworks are essential for enabling seamless communication and integration between disparate IoT devices and systems. Standardization efforts such as the Open Connectivity Foundation (OCF), the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC), and the Thread Group aim to define common protocols, interfaces, and data models to facilitate interoperability and compatibility across IoT ecosystems. By embracing interoperability and standardization, organizations can unlock new opportunities for collaboration, innovation, and scalability in the IoT landscape.
Selecting the Right IoT Device Management Platform
In this section, we'll discuss the factors to consider, evaluation criteria, case studies and success stories, and provide a checklist to guide your decision-making process.
1. Factors to Consider:
Scalability: Assess the platform's ability to scale with your IoT deployment, accommodating growth in the number of devices and data volume.
Security: Prioritize platforms with robust security features, including encryption, access control, and threat detection, to safeguard sensitive data and mitigate cyber threats.
Interoperability: Ensure compatibility with existing IoT devices, protocols, and standards to facilitate seamless integration and interoperability.
Flexibility: Look for platforms that offer customization options and support for diverse use cases, allowing you to tailor the solution to your specific requirements.
Ease of Use: Evaluate the platform's user interface, management tools, and documentation to ensure usability and ease of adoption for your team.
Cost: Consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses, to determine the platform's affordability and ROI.
2. Evaluation Criteria:
Feature Set: Assess the platform's capabilities, including device provisioning, configuration management, over-the-air updates, monitoring, and diagnostics.
Reliability: Evaluate the platform's uptime, reliability, and performance to ensure uninterrupted operation and minimal downtime.
Support and Maintenance: Consider the vendor's support offerings, including technical support, training, and updates, to ensure timely assistance and ongoing maintenance.
Integration: Determine the platform's compatibility with your existing systems, applications, and cloud platforms to facilitate seamless integration and data exchange.
Scalability: Verify the platform's scalability and performance under load to accommodate future growth and increasing demand.
Security: Assess the platform's security features and protocols to protect against cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
3. Case Studies and Success Stories:
Review case studies and success stories from other organizations that have implemented the platform to understand its real-world applications, benefits, and outcomes. Look for organizations with similar use cases, industries, and challenges to gain insights into the platform's effectiveness and suitability for your needs.
4. Checklist for Decision Making:
Develop a checklist of requirements, priorities, and evaluation criteria to guide your decision-making process.
Compare multiple platforms against your checklist, considering factors such as scalability, security, interoperability, and cost.
Seek input from stakeholders, including IT teams, business units, and end-users, to ensure alignment with organizational goals and requirements.
Conduct proof-of-concept trials or pilot deployments to assess the platform's suitability, performance, and ease of use in a real-world environment.
Obtain quotes, proposals, and references from vendors, and perform due diligence to ensure the selected platform meets your needs and delivers value.
Conclusion
In concluding this comprehensive guide on IoT device management, it's evident that the landscape is evolving rapidly, presenting both challenges and opportunities for organizations. As we've explored the fundamental concepts, key features, business benefits, and future trends in IoT device management, it's clear that strategic decision-making and continuous innovation are crucial for success in this dynamic field. Looking ahead, embracing emerging technologies such as AI, edge computing, and blockchain, while prioritizing security, interoperability, and scalability, will be essential for staying ahead of the curve. Encouraging further exploration, collaboration, and skill development will empower organizations to harness the full potential of IoT device management and drive transformative change in their operations and offerings.